Lecture 33-34 Preview
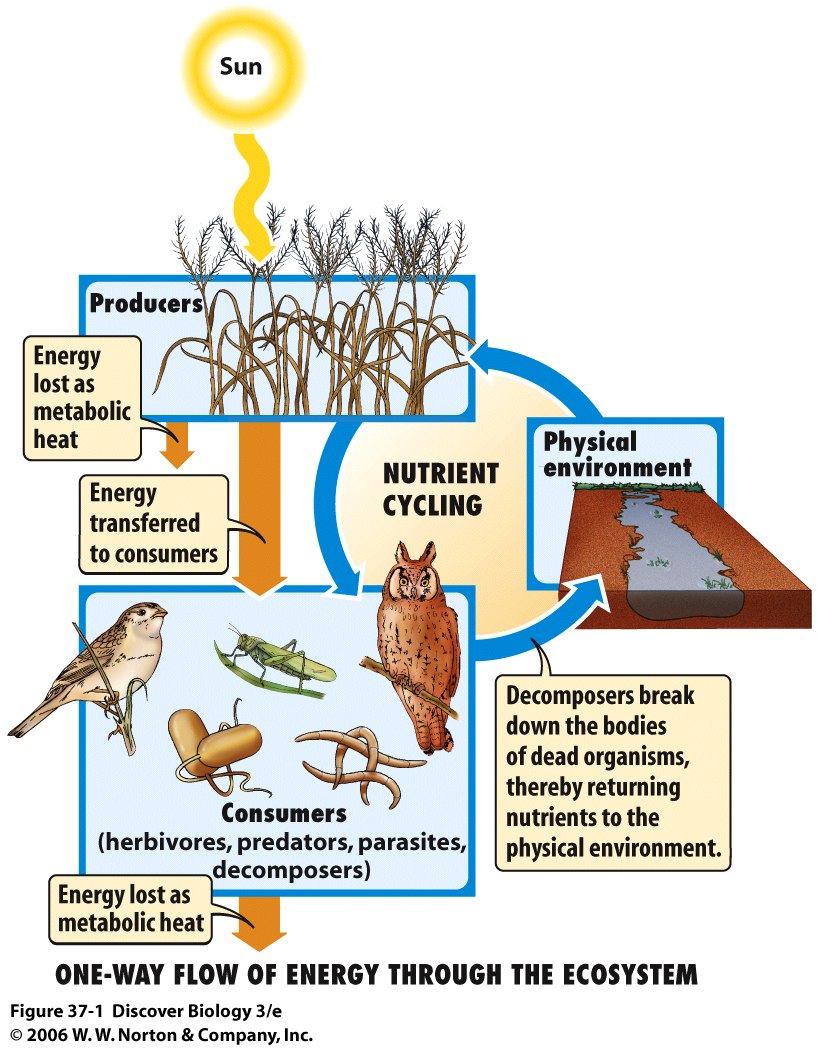
Within every kind of ecosystem energy flows one way through the living things. It enters as light and exits as heat.
Matter cycles back and forth between biotic and abiotic parts of the ecosystem.

Remember that energy is not created or destroyed, but changed from one form to another. Living things get energy either by converting light energy to chemical energy in glucose or consuming chemical energy in organic molecules. Living things use energy to move themselves, build new molecules, move molecules in cells. With each energy use some energy is converted to heat, which cannot be used to move and build molecules.
Because some energy is lost as heat with energy use, only about 10% of the energy taken in by a trophic level is available for consumption by the next trophic level. Energy pyramids result.
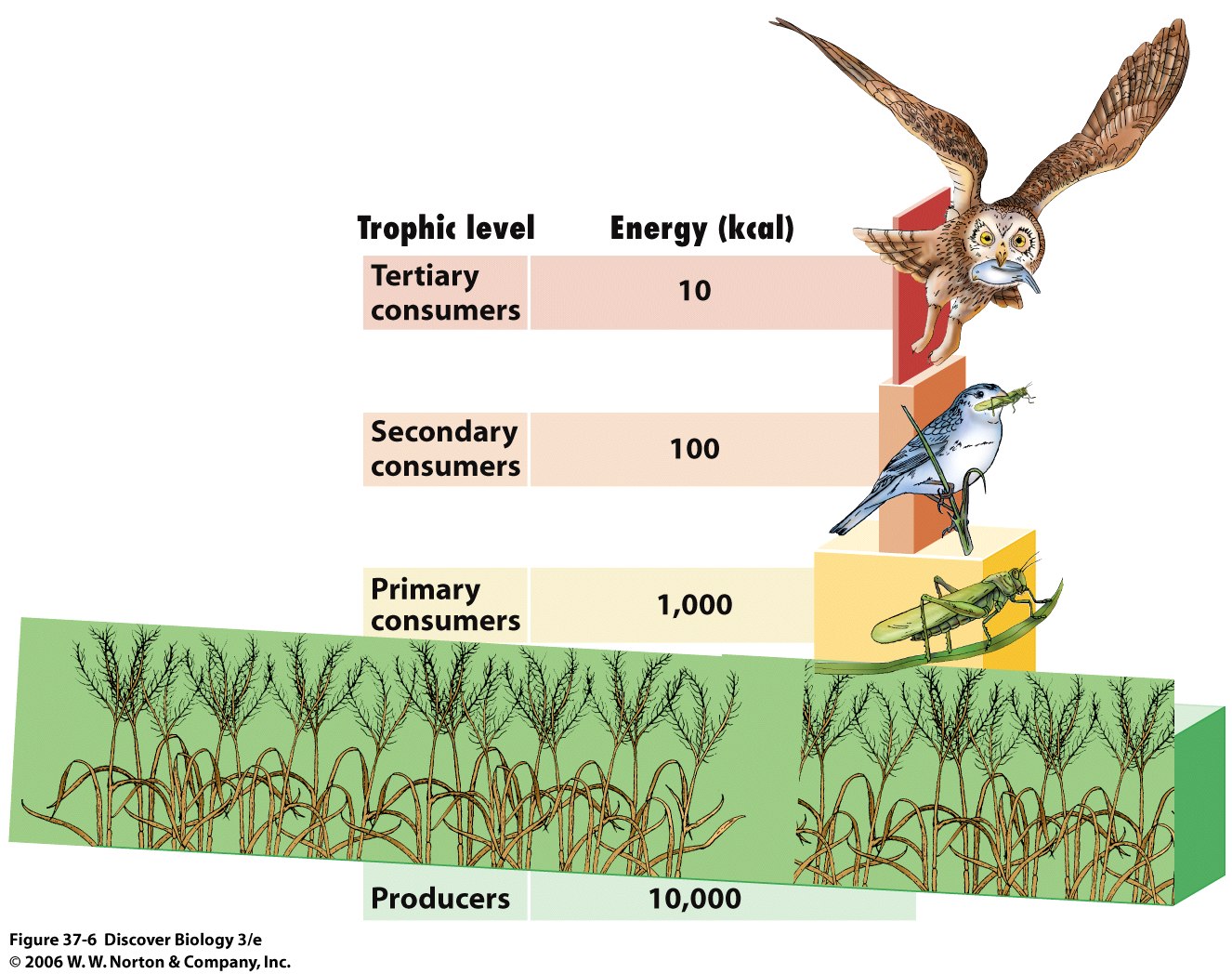
How would a producer use energy so that it would be edible by the next trophic level (available as food)?
How would a producer use energy so that it would not be edible by the next trophic level (not available as food)?
How would a primary consumer use energy so that it would be edible by the next trophic level?
How would a primary consumer use energy so that it would not be edible by the next trophic level?
Why are quaternary consumers (consumers of tertiary consumers) rarely found?
Within all kinds of ecosystem matter (atoms, ions, molecules) cycle through the living and non-living parts of the ecosystem. The cycles are called biogeochemical cycles. Humans have a large impact on the distribution of matter in these cycles.
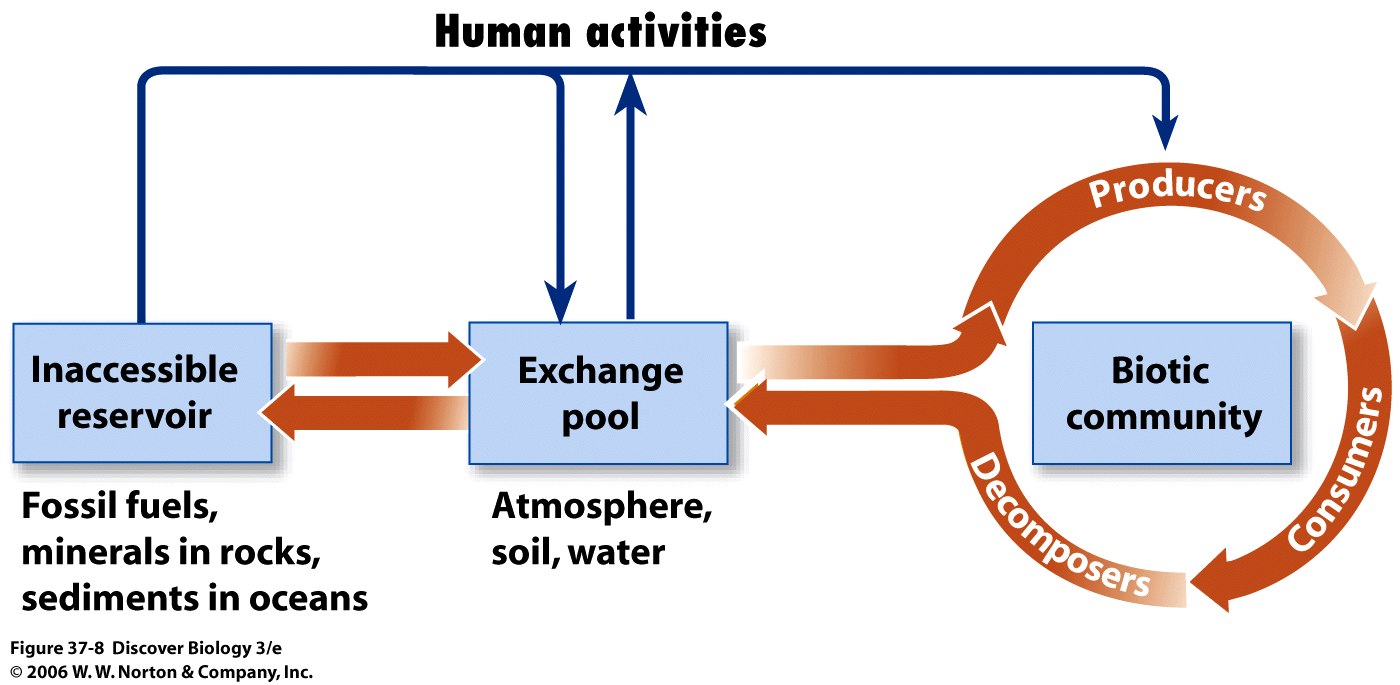
The carbon cycle is one kind of biogeochemical cycle.

What are the abiotic reservoirs of carbon in the ecosystem?
What are the biotic reservoirs of carbon in the ecosystem?
By what process does carbon move from the abiotic to the biotic reservoirs?
By what process does carbon move from the biotic to the abiotic reservoirs?
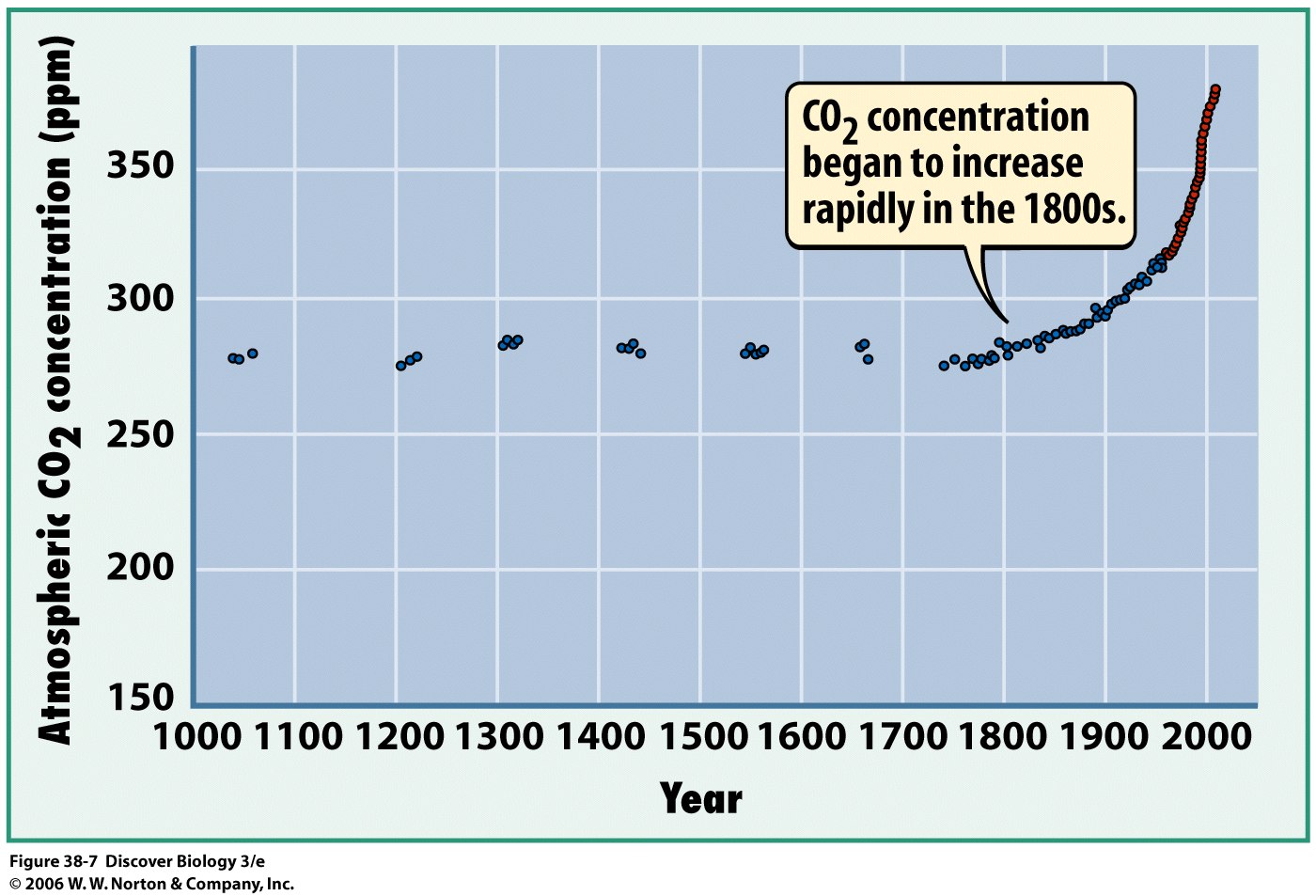
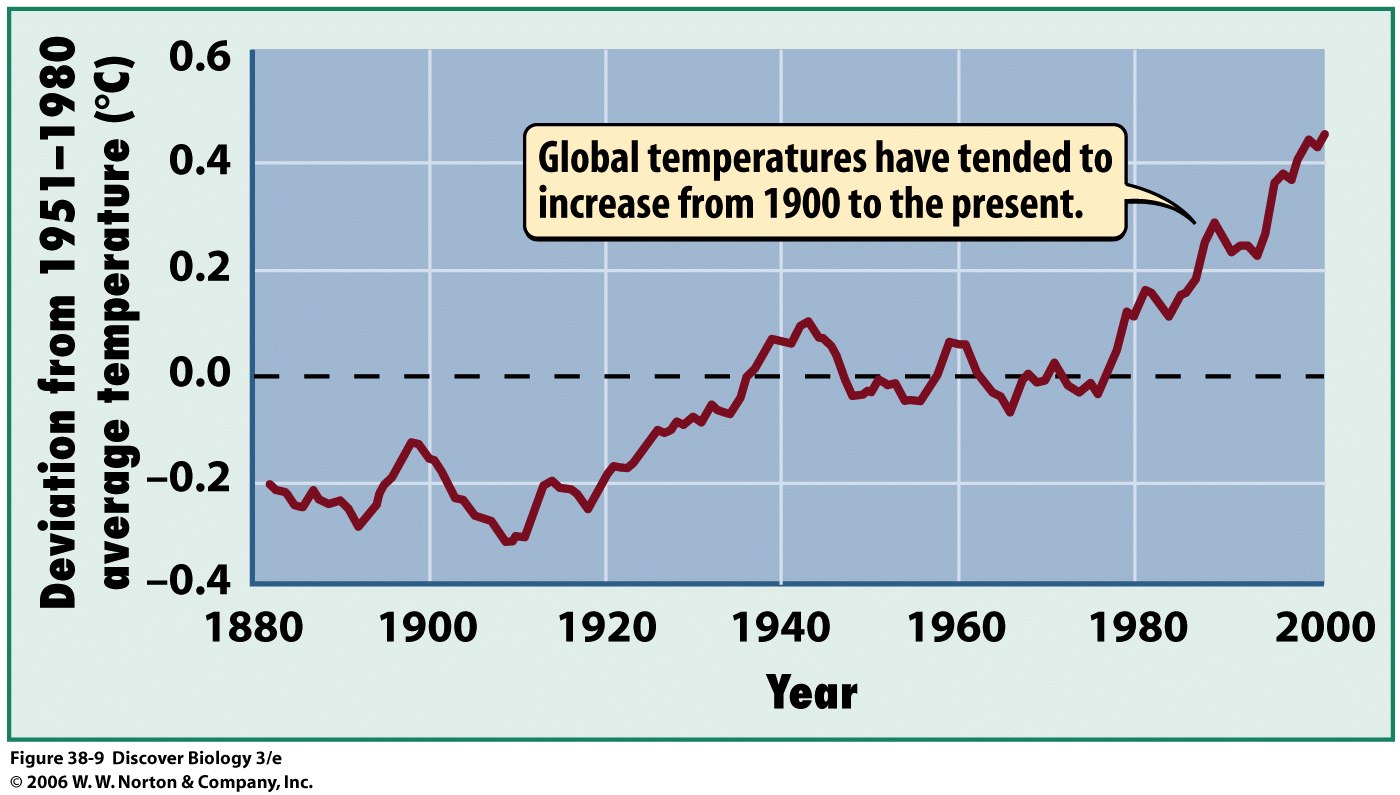
Too much carbon in the form of atmospheric carbon dioxide may be contributing to global warming. Atmospheric carbon dioxide prevents heat from leaving the surface of the earth, like a greenhouse traps heat in a garden. Ever left your car with the windows up on a sunny day?
The water cycle is a biogeochemical cycle.
What are the abiotic reservoirs of water in the ecosystem?
What are the biotic reservoirs of water in the ecosystem?
By what process does water move from the abiotic to the biotic reservoirs?
By what process does water move from the biotic to the abiotic reservoirs?