
BIO 7: Lecture 13 Preview
There are many ways to be a successful organism, as seen in the many different species that have been identified.

What are advantages of being small? What are disadvantages of being small?
What are advantages of being large? What are disadvantages of being large?
Large organisms require more organization
cells ---> tissues ---> organs ----> organ systems---> whole organism
Plants have 3-4 main types of tissues: dermal, vascular, ground, (meristematic)
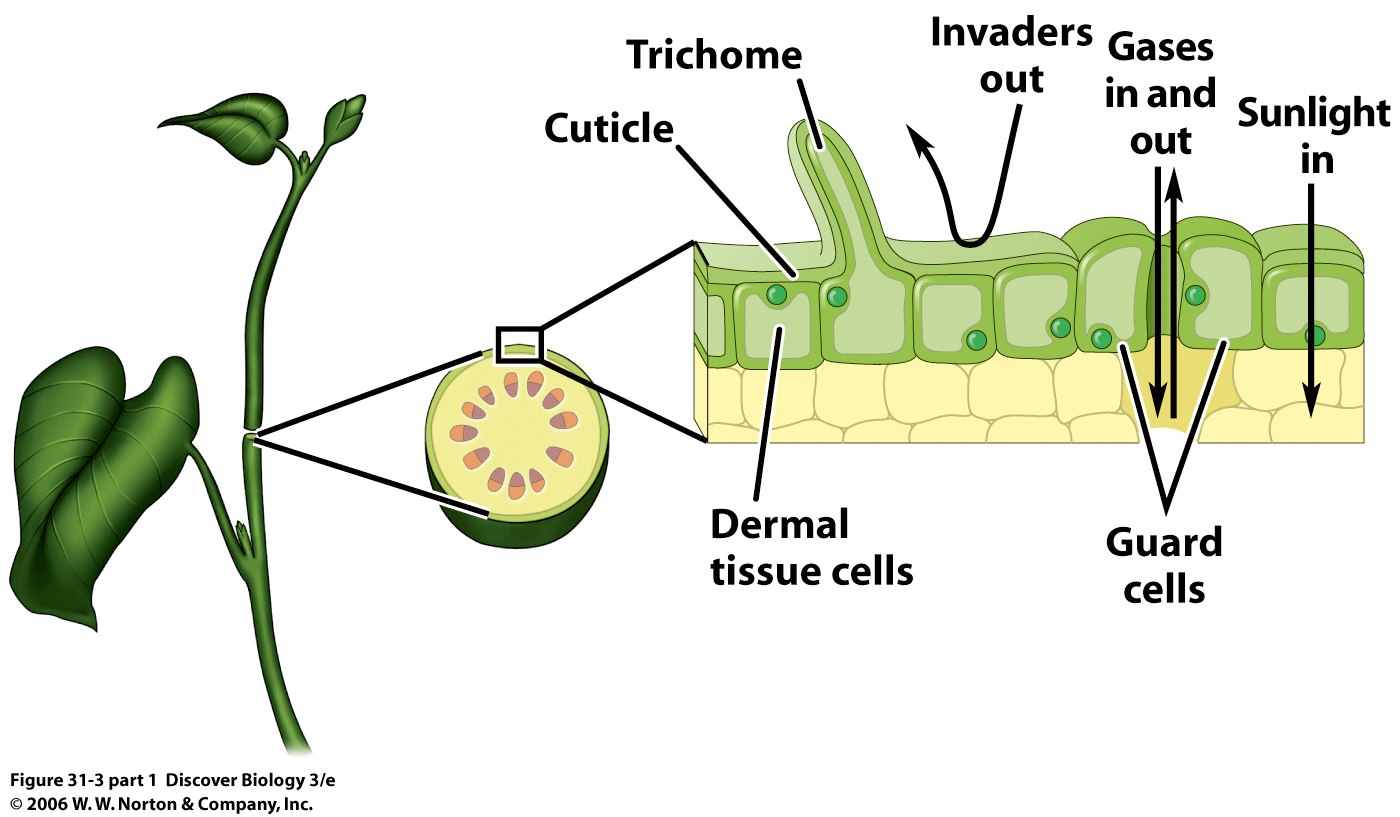
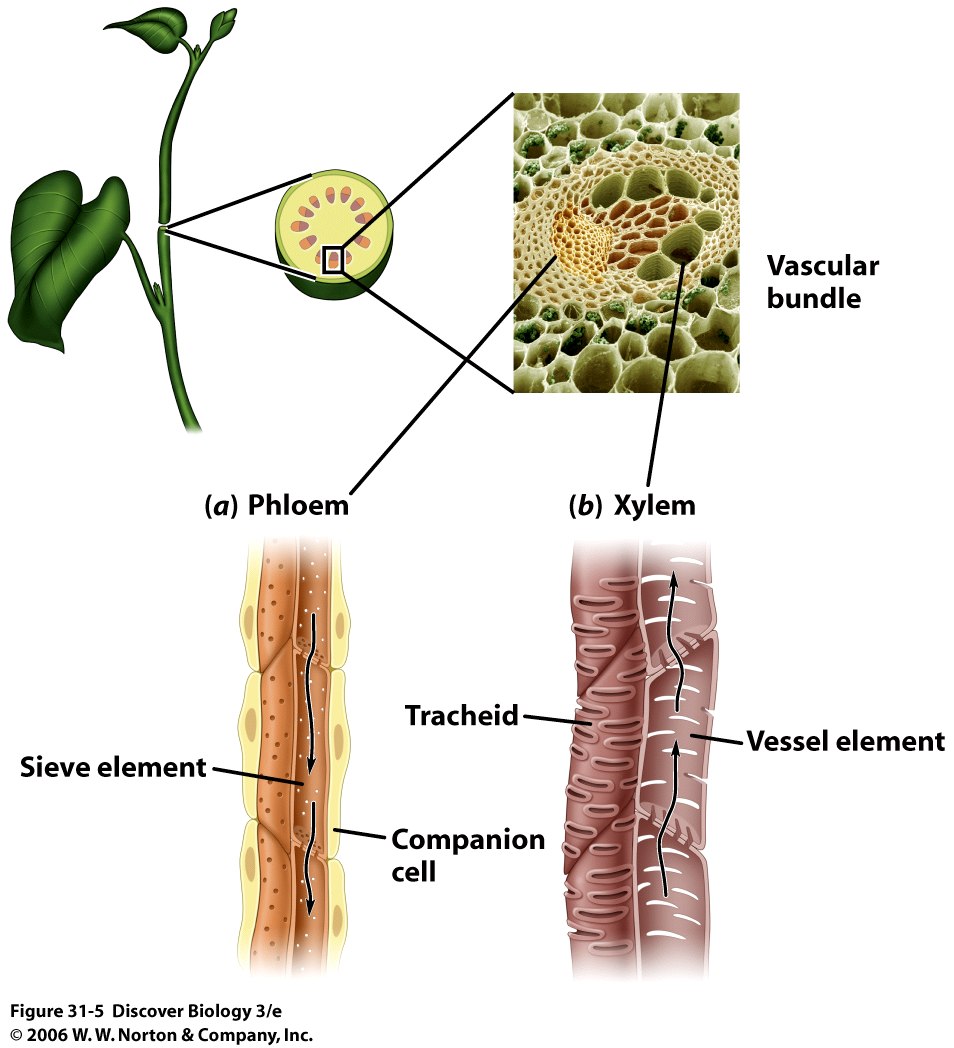
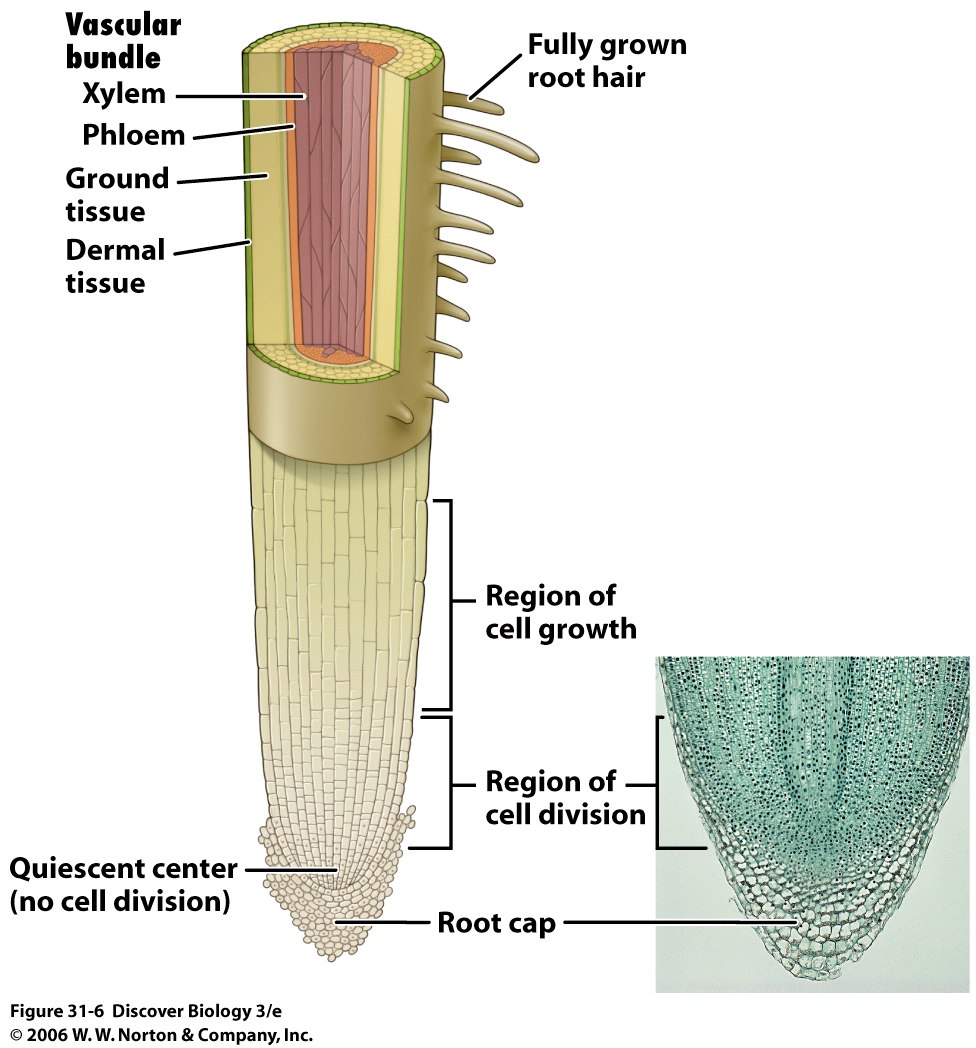
Plant Tissues are organized into 3-4 main organs: leaves, stems, roots, (flowers)
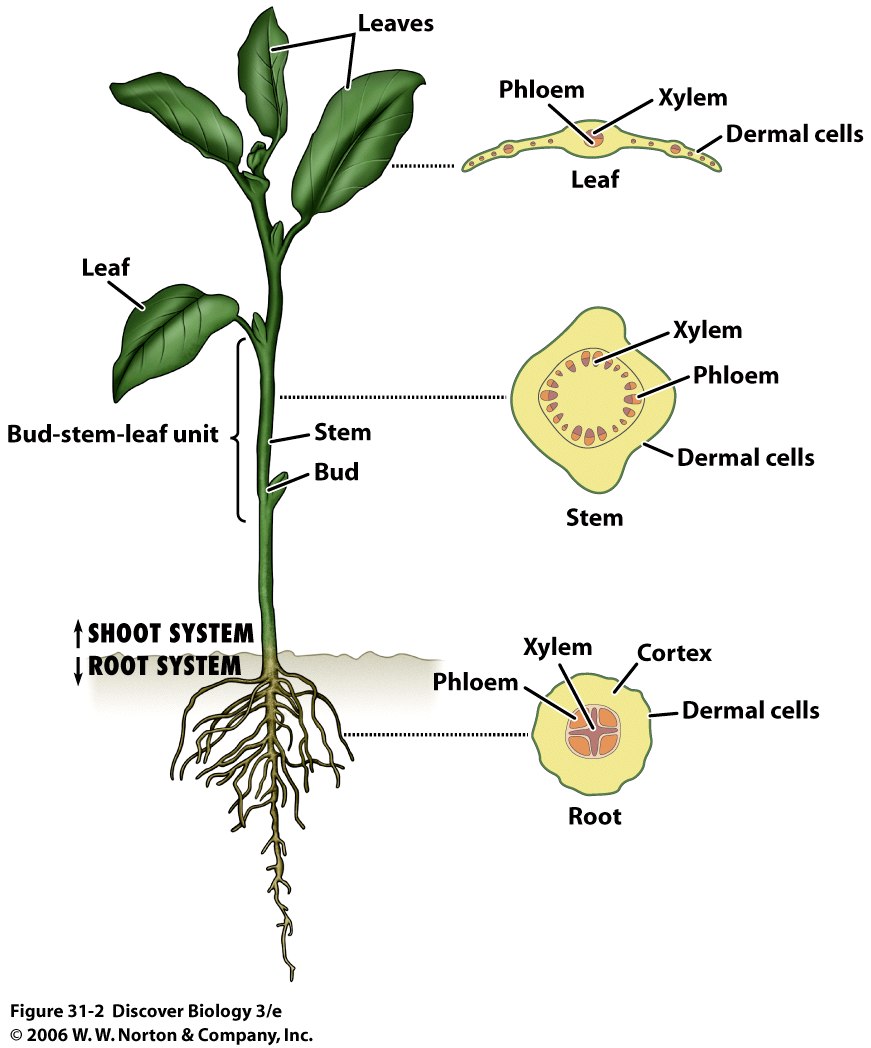
Plant Organs are organized into 2 main systems: shoots, roots
There are 4 basic types of Animal Tissues; cells forming tissues have specialized structures and functions.
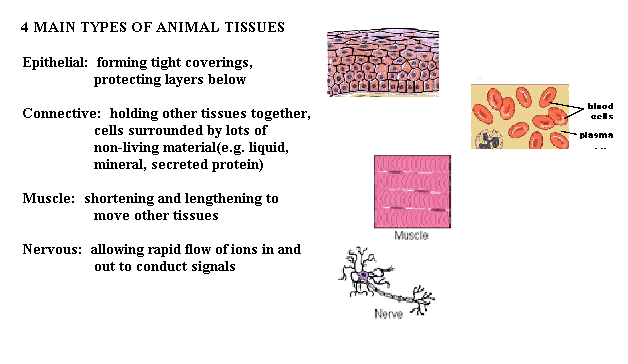
Organs are 2 or more different tissues working together to carry out a special function. Different organs work together in organ systems.
Animals commonly have 10 major organ systems. Their main functions and organs are summarized at this site.
http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/NSC/14-anatomy.htm
Time for Another Poster Assignment
In the second part of this class we are looking at large organisms and their tissues, organs, and organ systems. Information to make and operate these parts has been passed on in the DNA, mutations have resulted in some modifications, and those organisms with the modifications best suited for their environments have survived to reproduce more individuals carrying the successful information.
To learn more about organs and systems, you will be working in 8 different groups of 5-6 people. While hearing and reading about the general design of organ systems of successful organisms, each group will investigate a successful organism near to us in Sacramento:
ü An invertebrate living in the water: a zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha).
ü An invertebrate living on land: a honey bee (Apis mellifera).
ü A vertebrate (or chordate) living in the water: a Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha).
ü A vertebrate living on land: a California condor (Gymnogyps californianus).
For each animal, the group will prepare a poster with the following information (including citations).
For three of the design features (bullets 2-9) you will need to discuss what the advantages and disadvantages of the organism’s particular design features are.
I will be introducing the systems over the next two weeks (March 18-April 8). You will need to access outside sources about the specific organisms; the lectures should help give you some perspective on advantages and disadvantages of different designs.
Group members will receive the same basic score, which will then be adjusted based on Peer Evaluations.