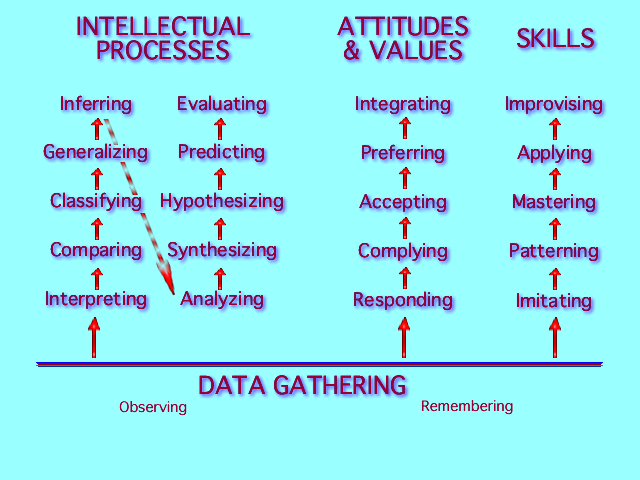
Click on any Intellectual Process, Attitude and Value, or Skill for a brief explanation.

DATA GATHERING: Observing and Remembering are the two basic abilities that students use to generate data and build a knowledge base in all subjects and at all levels of instruction. Selective retrieval of information from memory and the collection of new data through observation are prerequisite and provide the content and know-how that are essential to the attainment of other intellectual, affective and skill objectives.
Observing: The student identifies and describes elements from observations conducted with a purpose in mind.
Remembering: The student recalls or recognizes information from memory.
INTELLECTUAL PROCESSES:
Interpreting: The student explains the meaning and states the significance of data observed or remembered.
Comparing: The student identifies observed similarities and differences in objects or activities.
Classifying: The student groups, sorts, or places items into categories based on apparent or identified characteristics or criteria.
Generalizing: The student expresses a conclusion drawn from the consideration of a number of specific instances.
Inferring: The student goes beyond the data studied and applies a prior generalization to a parallel situation.
Analyzing: The student critically studies material to examine elements, relationships, or principles of organization.
Synthesizing: The student combines parts into a meaningful whole, integrates them, creates a new product, rule, or theory.
Hypothesizing: The student formulates a means of testing or further investigating a rule, principle, or theory that has been proposed or generally accepted.
Predicting: The student forecasts or anticipates what may happen in the future employing a rule, principle, or theory as a guide.
Evaluating: The student makes a judgment of the merit, value, or worth of an object, proposition, action, or activity in terms of defined criteria or standards.
ATTITUDES AND VALUES:
Attending: The student directs attention to instruction and to the task at hand.
Responding: The student actively reacts to directions and to the task at hand.
Complying: The student carries out instructions and completes the task at hand.
Accepting: The student finds worth in a behavior, act, idea, or position.
Preferring: The student selects behaviors, acts, ideas or positions after considering alternatives.
Integrating: The student incorporates value-based behavior into a pattern that is becoming part of his or her life style.
SKILLS:
Imitating: The student copies each element of a behavior or act while following a model and is provided with direct assistance.
Patterning: The student executes a behavior or act in identified situations with precision and appropriate speed.
Mastering: The student executes a behavior or act in identified situations with precision and appropriate speed.
Applying: The student uses a skill independently in a variety of situations and with precision and appropriate speed.
Improvising: The student modifies, adapts, or introduces new elements to a previously learned skill.