Higher Visual Processing
Visual Cortex (area V1(& V2)):
Hubel and Wiesel (1959)
Types of Cortical Cells:
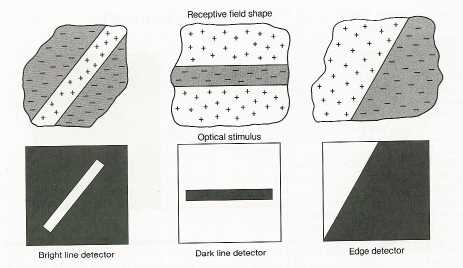
1. Simple Cortical Cells:
e.g.

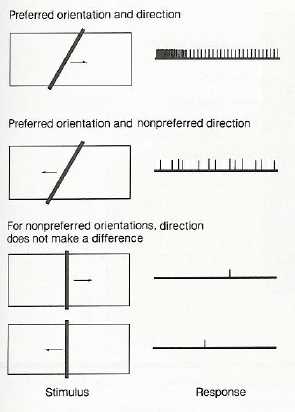
2. Complex Cortical Cells:
e.g.
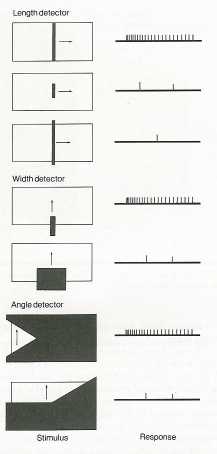
3. End-Stopped Cells: (a.k.a. feature detectors)
e.g.
Organization of Cortical Cells:
1. Location Columns:
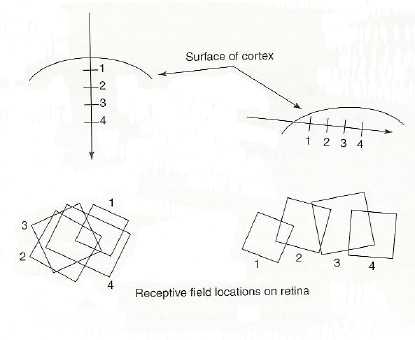
2. Orientation Columns:
3. Ocular Dominance Columns:
4. Hypercolumns -

Extrastriate Cortex (areas beyond the primary visual cortex(V1) -- V3, V4, & V5)
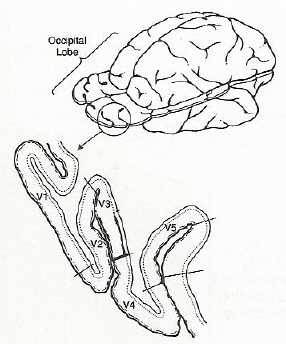
Different processing pathways for different pieces of information.
A. Form channel (V3):
visual form agnosia:
e.g.
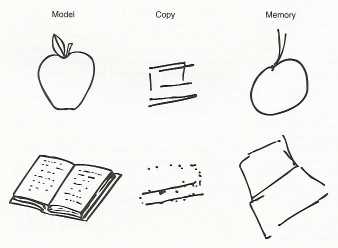
e.g. prosopagnosia--
B. Color channel (V4):
stroke patients
C. Motion channel (V5):
Object Perception
Gestalt Approach to Object Perception: (gestalt means "whole" or "shape")
"The whole is different than the sum of its parts."
Figure and Ground:
e.g. ball resting on a grassy field
ball =
grass =
e.g.
Factors that determine what is seen as figure and ground:
Oyama (1960) -
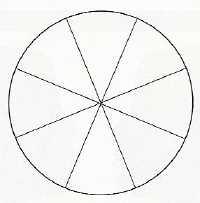 = same
size
= same
size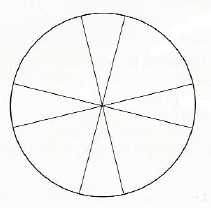 =
smaller size
=
smaller size
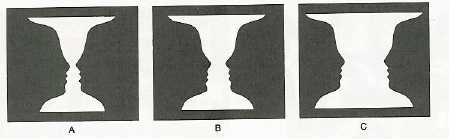

Examples of Ambiguous Figure/Ground:
e.g. Escher
Illusory Contours:
e.g.
More complex illusory contours -
contours can vanish due to how we interpret the visual stimlulus (top down processing)
e.g. necker cube figure
Gestalt Principles of Organization:
1. Proximity:
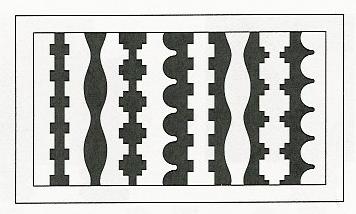
2. Similarity:
3. Good Continuation:
4. Common Fate: (Law of common motion)
5. Closure:
6. Pragnanz:
Modern Gestalt Principles:
7. Common Regions:
8. Element Connectedness:
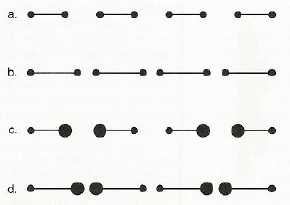
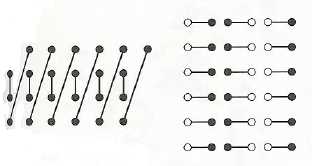
9. Synchrony:
e.g. flashes of light
Visual System Wants to Organize Visual Scene