Name_________________________
California State University, Sacramento
Economics 100B-Sample Midterm 3
1) General equilibrium analysis is the study of
A) how an equilibrium is determined in all markets simultaneously.
B) how an equilibrium is determined in all closely related markets.
C) the effects of a change in a market, and all spillover effects in all related markets.
D) All of the above.
2) Joe and Rita each have some milk and cookies. Joe's MRS of cookies for milk is 2. Rita's MRS of cookies for milk is 4. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) No gains from trade are possible.
B) Both Rita and Joe can be made better off if Rita gives Joe some cookies in exchange for milk.
C) Rita and Joe are on the contract curve.
D) Both Rita and Joe can be made better off if Joe gives Rita some cookies in exchange for milk.
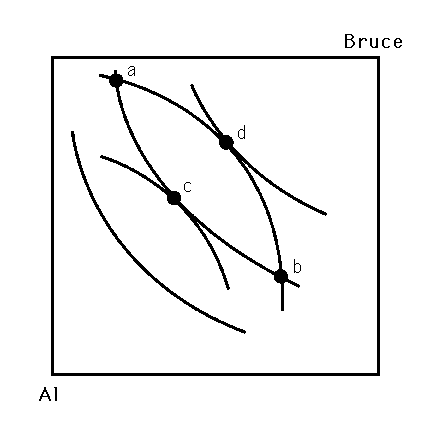
Figure 10.1

3) Figure 10.1 depicts the Edgeworth box for two individuals, Al and Bruce. The contract curve can found by connecting points
A) a and b.
B) a and c.
C) b and d.
D) c and d.
4)Whenever two indifference curves in figure 10.1 cross, the immediate result is
A) Pareto optimality C) inefficient allocation resources
B) Inefficient allocation goods D) bliss
5) If only two people are trading their endowments and no production is possible, then
the equilibrium they reach will
A) be on their contract curve.
B) result in unequal marginal rates of substitution for the two people.
C) result in one person being worse off than with his or her endowment.
D) All of the above.
6) For a given set of prices, two consumers choose bundles that are off the contract curve. In a competitive market,
A) prices will adjust until the consumers choose bundles that are on the contract curve.
B) the indifference curves will shift back to the contract curve.
C) the contract curve will shift to connect these bundles.
D) no adjustments need to be made.
7) Figure 10.1 depicts the Edgeworth box for two individuals, Al and Bruce. If the endowment is at point a, and Al has no ability to bargain, the final allocation will be at point
A) a. C) c.
B) b. D) d.
8) If everyone's utility is given equal weight and a change in resource allocation results in one person's gain exceeding another person's loss, we can say that the new allocation
A) is Pareto superior to the original one.
B) increases social welfare.
C) decreases social welfare.
D) is efficient.
9) Gains from trade can only occur when
A) marginal rates of substitutions differ across people.
B) marginal rates of substitution are equal across people.
C) indifference curves are convex.
D) people find themselves on the contract curve.
10) Moving away from the contract curve will
A) harm both parties.
B) harm only one of the parties.
C) harm at least one of the parties.
D) harm neither of the parties.
11) “Any competitive equilibrium is Pareto efficient because, with a competitive
equilibrium the slope of the price line equals the MRS for all consumers.”
A) True
B) False
12) For a given set of prices, two consumers choose bundles that are off the contract curve. In a competitive market,
A) prices will adjust until the consumers choose bundles that are on the contract curve. Duplicate question..2 points automatically awarded. Question not scored.
B) the indifference curves will shift back to the contract curve.
C) the contract curve will shift to connect these bundles.
D) no adjustments need to be made.
13) If pizza is measured on the horizontal axis and pretzels are measured on the vertical axis, the slope of the production possibility frontier at a given combination reflects
A) the total cost of producing that combination.
B) the total cost of producing that quantity of pizza in terms of pretzels.
C) the cost of making the last pizza in terms of pretzels.
D) the cost of making the last pretzel in terms of pizza.
14) If the inverse demand function for a monopoly's product is p = a - bQ, then the firm's marginal revenue function is
A) a.
B) a - (1/2)bQ.
C) a - bQ.
D)a - 2bQ.
15) The government prefers an ad valorem tax to a specific tax that reduces the monopoly output by the same amount because
A) consumers are not harmed by the ad valorem tax.
B) the monopoly prefers the ad valorem tax.
C) consumers prefer the ad valorem tax.
D) the ad valorem tax transfers more revenue from the monopoly to the government
16) Government actions that create monopolies
A) spur product innovation by the monopoly.
B) create deadweight loss.
C) result in lower average costs of production.
D) ensure that firms price at marginal cost.
17) A dominant firm's residual demand curve is
A) the horizontal difference between the market demand curve and the supply curve of the fringe firms.
B) the vertical difference between the market demand curve and the supply curve of the fringe firms.
C) the demand curve left for the fringe firms after the dominant firm has determined an output level.
D) None of the above.
18) Which of the following conditions must be true so that a firm can price discriminate?
A) There are no other firms in the market.
B) The good is a non-durable.
C) The good cannot be easily resold.
D)All of the above.
19) A perfect price discriminator
A) charges each buyer her reservation price.
B) charges different prices to each customer based upon different costs of delivery.
C) generates a deadweight loss to society.
D) charges lower prices to customers who buy greater quantities.
20) If a market is controlled by a perfect-price-discriminating monopoly, then
A) a deadweight loss is generated.
B) there is no consumer surplus.
C) consumer surplus is the same as under perfect competition.
D)output is less than that of a single-price monopoly.
21) Perfect competition and monopolistic competition are similar in that both market structures include
A) price-taking behavior by firms.
B) a homogeneous product.
C) no barriers to entry.
D) very few firms.
22) Regardless of market structure, all firms
A) consider the actions of rivals.
B) maximize profit by setting marginal revenue equal to marginal cost.
C) produce a differentiated product.
D) have the ability to set price.
Figure 13.1
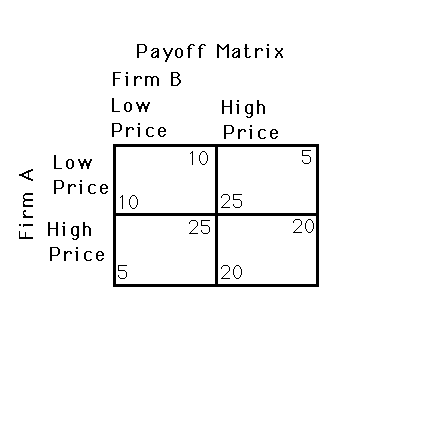
23) Figure 13.1 shows a payoff matrix for two firms, A and B, that must choose between a high-price strategy and a low-price strategy. For firm B,
A) setting a high price is the dominant strategy.
B) setting a low price is the dominant strategy.
C) there is no dominant strategy.
D) doing the opposite of firm A is always the best strategy.
24) “A low price strategy by both firms creates a Nash equilibrium.”
A) True B) False
25) If both firms, shown in Figure 13.1 colluded, then they would each follow a high price strategy.”
A) True B) False
26) A cartel is a group of firms that attempts to
A) maximize joint revenue.
B) maximize joint profit.
C) behave independently.
D)increase consumer surplus.
27) In a sense, a cartel is self-destructive because
A) it reduces consumer surplus.
B) it sets price above marginal cost.
C) each cartel member has the incentive to cheat on the cartel.
D)each cartel member earns economic profit.
28) Imagine reaction functions for two pizza shops in a small isolated town. The Cournot equilibrium is at point
A) one firm dominates the other
B) zero output
C) both firms share the market about equally
D)cannot be determined.
29) In the Cournot model, a firm maximizes profit by selecting
A) its output, assuming that other firms keep their output constant.
B) its price, assuming that other firms keep their price constant.
C) its output, assuming that other firms will retaliate.
D) its price, assuming that other firms will retaliate.
30) The Stackelberg model is more appropriate than the Cournot model in situations where
A) there are more than two firms.
B) all firms enter the market simultaneously.
C) one firm makes its output decision before the other.
E) firms will be likely to collude.
II. Short Answer
(15)
1)How does monopoly injure consumer surplus?
By setting price above marginal cost, output is reduced. Buyers who value the good by more than the incremental cost of making the good are not allowed to buy these incremental units. Welfare is diminished.
(15)
2) Assume that the inverse industry demand curve is P = 100 – Q. A monopoly produces all output in this industry.
a) Price elasticity of demand at a price of 75 is ___3____________.
b) Assuming no costs, profit is maximized when Q = __50________.
c) Assuming that marginal cost is a constant $10 per unit, then profit maximizing
Output is ______45_________ and profits are $_____2025__________.
(10)
1) Name one distinguishing characteristic of each industry listed below:
Perfect Competition ______price taking from the market__________________________
Monopolistic Competition____tangency solution_______________________________
Oligopoly_______________strategic interaction…price leadership and followship__________________________