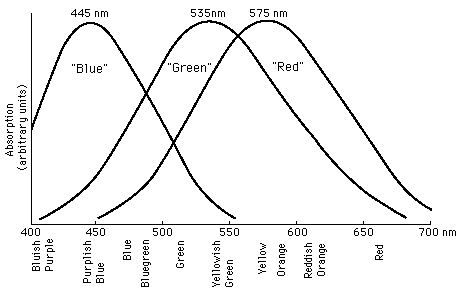
each receptor is sensitive to light from a different part of visual spectrum -- based on three different cone photopigments.
Blue:
Green:
Red:
Color Blindness results when don't have one type of cone receptor working.
Then we can only use 2 cone receptor types to determine color and it creates confusions.
e.g. red-green color blindness:
from 2 causes
1.
2.

e.g. yellow-blue color blindness: