Imagery
Imagery:
e.g.
Question #1: How do we form images?
1st showed people pictures
2nd showed pictures that were parts of the original pictures (good and odd).
Asked: Is this shape in the original drawing?
Results:
1)
2)
Conclusions:
1)
2)
Kosslyn , et. al (1988)
1st subjects were shown block capital letters and told they would need to image them later.
....
....etc
2nd shown a little letter with empty grid --cue to remember Capital letter.
3rd shown a blank grid on which 2 Xs appeared (after 500 ms--still forming image)
Task: say if the original block letter image would cover both the Xs.
Hypotheses:
1)
2)
feature of the experiment:
location of the Xs varied
Results:
1)
e.g.
2)
Conclusion:
Question #2: Can people mentally inspect images?
Image Inspection -
Experiment: Finke, Pinker, & Farah (1989)
Task: Try to follow set of oral instructions altering an image.
Visualize Letter Q
Put O next to it
Remove Diagonal Line
Rotate figure 90 degrees to the left-What is it?
Results:
Experiment: Bisiach and Luzzatti (1978)--
They investigated:
used subjects with "hemispatial neglect" disorder:
an attentional disorder
ignore half of visual field (usually left)
behaves as if one side of world does not exist
Method:
1st patients told to imagine themselves walking to the Piazza del Duomo (plaza in Italy)
and 2nd describe what they "see" along the way
Results:
Method cont.
3rd told to walk beyond the square and mentally turn around.
4th return to the square
Results:
Conclusions:
New Question Raised:
Experiment: Brandt and Stark (1997)
investigated eye movements in image scanning
Task:
1st showed people irregular checkerboards & said they would need to image it later.
They recorded their eye movements as the subject scanned the picture.
2nd told subject to image the picture (again they recorded eye movements).
Results:
Question #3: How do people manipulate or transform Images?
Image Rotation:
Experiment: Shepard & Metzler (1971)
Task:
1st see 2 objects (one rotated)
Subject answers: same or different
Results:
the more mental rotation needed the longer it takes to respond
Conclusions:
Related Question to #3: If scanning an image mirrors actual perception, does image transformation mirror actual object transformations?
Experiment 1: Cooper (1975)
Method:
1st subjects learned each image and what was considered normal vs. mirror-reversed.
Simple Complex
2nd - shown an image and need to respond if normal or mirror-reversed.
objects were rotated (either 0, 60, 120, or 180) from original orientation.
Results:
Conclusion:
Experiment 2: Parsons (1987)
Examined if physically harder transformations are also harder transformations mentally.
Method:
Results:
Conclusion:
Experiment 3: Freyd & Finke (1984)
Rotating objects have momentum.
Do images?
Method:
1st Subjects see rotating rectangle
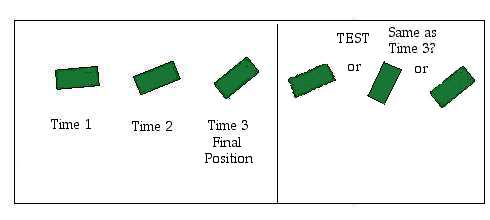
2nd told to remember the final position
3rd Then shown a picture of the rectangle.
orientation of picture varied.
Subjects asked: Is test stimulus same or different as Time 3?
Results:
undershot:
overshot:
Conclusion: