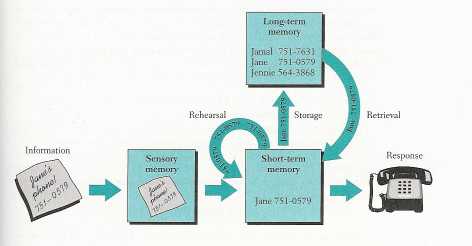
Long Term Memory
Atkinson & Shiffrin Model of Memory cont. (1968)
Long-term memory:

- Serial Position Effect -
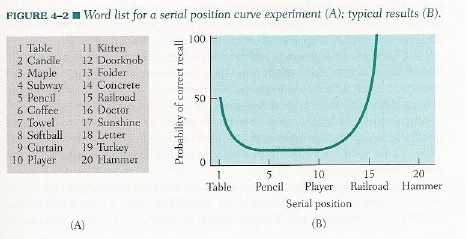
- Primacy effect -
- Recency effect -
Characteristics of LTM:
Ebbinghaus - 1st systematic research on memory (1885)
- nonsense syllables (BEF, RIL, etc)
- study until 100% accuracy in recall
- Free recall at different time intervals
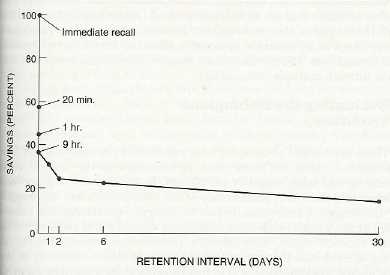
exp: Bahrick (1983) -
exp: Baddeley (1966)
list A: words that sounded similar
list B: words with similar meanings
list C: words that did not sound similar or have similar meanings (control group)
Task:
Results:
Conclusion:
Task: Paired Associates Learning -
- Proactive Interference (PI) -
| Phase | Experimental Group | Control Group |
| 1 | Flag - Spoon | (unrelated task) |
| 2 | Flag - Bike | Flag - Bike |
| Test | Phase 2 list | Phase 2 list |
| Results: |
- Retroactive Interference -
| Phase | Experimental Group | Control Group |
| 1 | Flag - Spoon | Flag - Spoon |
| 2 | Flag - Bike | (unrelated task) |
| Test | Phase 1 list | Phase 1 list |
| Results: |
- What is cause of interference?
- Anderson & Neely (1996)
Neurological Basis of Memory -
1)
2)
3)
Results:
Experiment 2:
Results of Experiment 2:
Conclusion:
- mass action - the brain works en masse.
- equipotentiality -
Humans:
2 types of amnesia occurred:
1. anterograde amnesia:
Several features:
- effects transfer of info to LTM, but working memory is intact
- effects memory regardless of modality
- it does not effect skilled performance
2.retrograde amnesia:
Several features:
- amount of time lost varies widely
- for head injuries, memories can be somewhat recovered
- "overlearned" information is typically intact
- Frontal Lobe - important for working memory